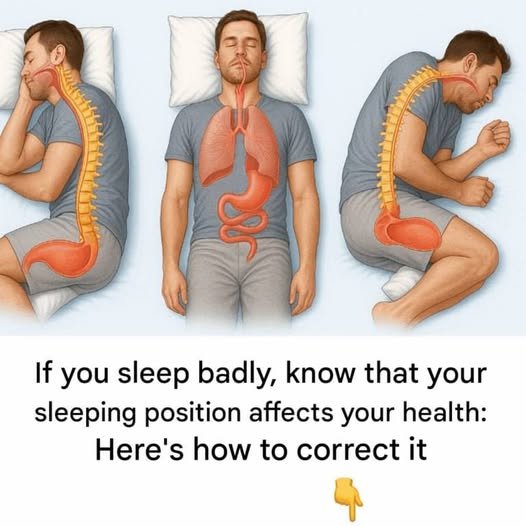
Sleeping in the Right Position: A Little-Known Secret for Your Well-Being
Sleep is often discussed in terms of duration—how many hours we should get each night—but far less attention is paid to how we sleep. According to sleep specialists, physical therapists, and doctors, sleeping position plays a major role in overall well-being, affecting everything from spinal health and digestion to breathing quality and energy levels.
Surprisingly, many common aches, poor sleep quality, and morning fatigue may not be caused by stress or aging alone, but by sleeping in the wrong position night after night. Understanding the impact of sleep posture can be a simple yet powerful way to improve daily health.
Why Sleeping Position Matters More Than You Think
When you sleep, your body spends 6–9 hours in a fixed position, which directly affects:
-
Spinal alignment
-
Blood circulation
-
Breathing efficiency
-
Digestive comfort
-
Muscle and joint recovery
Poor alignment during sleep can place unnecessary strain on the neck, shoulders, hips, and lower back. Over time, this can contribute to stiffness, headaches, nerve compression, and restless sleep.
Doctors emphasize that sleeping posture is not about perfection, but about supporting the body’s natural alignment.
The Most Common Sleeping Positions Explained
1. Back Sleeping (Supine Position)
Sleeping on your back is often considered one of the healthiest positions—when done correctly.
Potential benefits:
-
Keeps the spine, neck, and head aligned
-
Reduces pressure on joints
-
Helps prevent facial wrinkles caused by pillow compression
Potential drawbacks:
-
Can worsen snoring or sleep apnea
-
May increase lower back discomfort without proper support
Best practice:
Use a pillow that supports the natural curve of the neck and consider placing a small pillow under the knees to reduce pressure on the lower back.
2. Side Sleeping (Especially Left Side)
Side sleeping is the most popular position worldwide, and doctors often recommend it for multiple health reasons.
Potential benefits:
-
Supports spinal alignment when knees are slightly bent
-
May reduce acid reflux, especially on the left side
-
Can improve breathing and reduce snoring
Left-side sleeping, in particular, is often associated with:
-
Better digestion
-
Reduced pressure on internal organs
-
Improved circulation
Best practice:
Use a firm pillow between the knees to keep hips aligned and a pillow that fills the space between the mattress and your neck.
3. Right-Side Sleeping
Right-side sleeping shares many benefits with left-side sleeping but may not be ideal for everyone.
Possible considerations:
-
May increase acid reflux symptoms in some people
-
Still supportive for spinal health if properly aligned
Doctors suggest listening to your body and alternating sides if comfortable.
4. Stomach Sleeping (Prone Position)
Sleeping on your stomach is generally not recommended by specialists.
Why it can be problematic:
-
Forces the neck into an unnatural twisted position
-
Places strain on the lower back
-
Compresses internal organs
However, some people find it difficult to sleep any other way.
Best practice if unavoidable:
Use a very thin pillow or none at all and place a pillow under one hip to reduce spinal strain.
How Sleeping Position Affects Common Health Issues
Back and Neck Pain
Improper sleeping posture is one of the most overlooked causes of chronic stiffness and soreness. Supporting the spine in a neutral position allows muscles to relax and recover.
Digestion and Acid Reflux
Doctors often recommend left-side sleeping for people with digestive discomfort, as gravity helps keep stomach acid where it belongs.
Breathing and Snoring
Side sleeping can help keep airways open, improving airflow and reducing snoring in some individuals.
Circulation
Balanced sleep posture helps avoid pressure on blood vessels, reducing numbness or tingling in arms and legs.
The Role of Pillows and Mattresses
Sleeping position alone isn’t enough—supportive sleep tools matter.
Doctors recommend:
-
A pillow that matches your sleep position
-
A mattress that supports spinal alignment without being too soft or too firm
The right combination can dramatically improve sleep quality without changing sleep duration.
Why Small Changes Can Make a Big Difference
Many people assume discomfort is inevitable, but sleep specialists note that minor adjustments—such as pillow placement or side switching—can lead to noticeable improvements within days.
Better sleep posture may contribute to:
-
Reduced morning stiffness
-
Improved sleep continuity
-
Increased daytime energy
-
Better long-term joint health
These benefits accumulate gradually but consistently.
How to Train Yourself to Sleep Better
Changing sleep position doesn’t happen overnight. Doctors suggest:
-
Making gradual adjustments
-
Using pillows to support new positions
-
Allowing your body time to adapt
Consistency is key—your body learns patterns just like habits.
Final Thoughts
Sleeping in the right position is a simple, often overlooked secret to better well-being. While it may not replace medical care or lifestyle changes, it plays a powerful supporting role in how the body heals, rests, and functions daily.